
The incubation period can vary between a few weeks to many months, and is largely dependent on the number of hookworm parasites an individual is infected with. The lesions are typically intensely itchy. With advancing movement of the larvae, the rear portions of the lesions become dry and crusty. The larvae migrate in tortuous tunnels between the stratum basale and stratum corneum of the skin, causing serpiginous vesicular lesions. This infection is due to larvae from the A. The hosts of these worms are not human and the larvae can only penetrate the upper five layers of the skin, where they give rise to intense, local itching, usually on the foot or lower leg, known as ground itch.
#How big are hookworms in humans skin#
Larval invasion of the skin (mostly in the Americas) can produce a skin disease called cutaneous larva migrans also known as creeping eruption. Signs of advanced severe infection are those of anemia and protein deficiency, including emaciation, cardiac failure, and abdominal distension with ascites. Epigastric pains, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea can occur early or in later stages, as well, although gastrointestinal symptoms tend to improve with time.
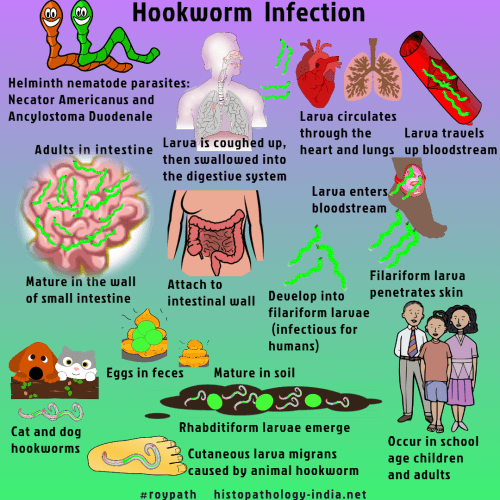
Coughing, chest pain, wheezing, and fever sometimes result from severe infection. No symptoms or signs are specific for hookworm infection, but they give rise to a combination of intestinal inflammation and progressive iron-deficiency anemia and protein deficiency.
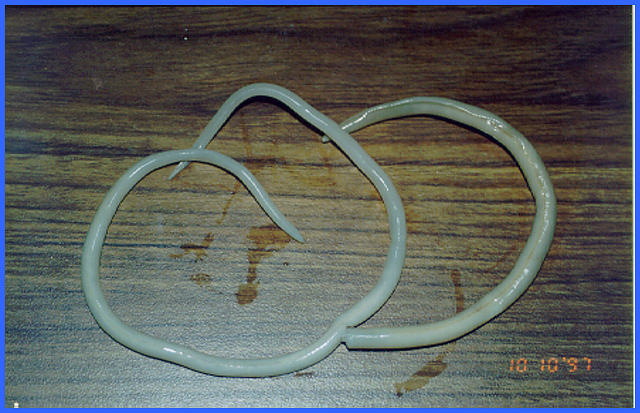
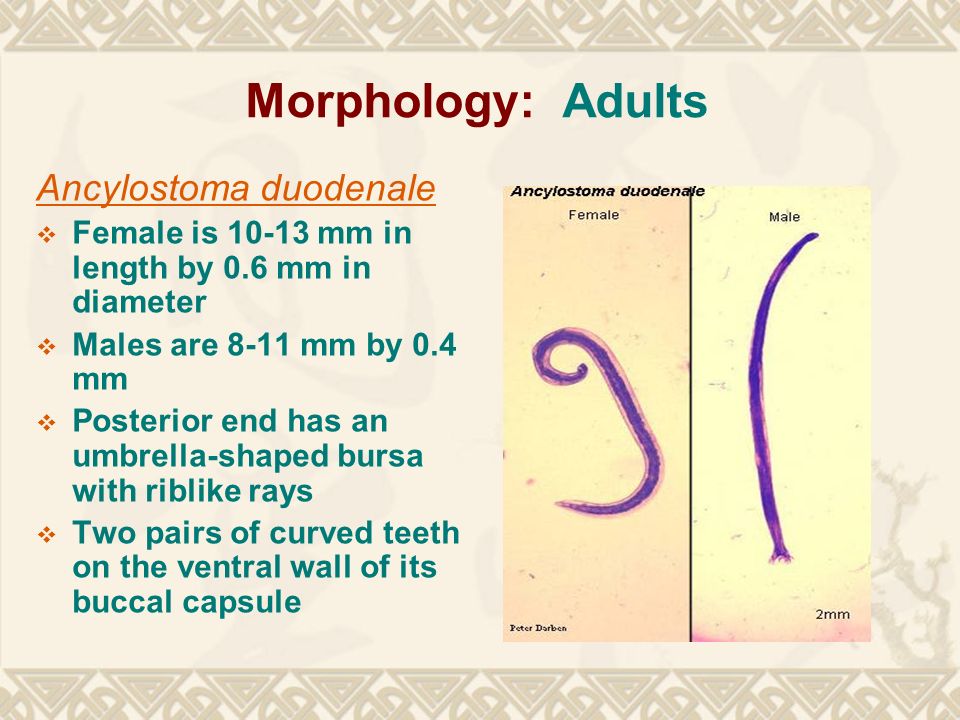
The mental and physical development of children may be affected. Those infected by many worms may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and tiredness. Those only affected by a few worms may show no symptoms. Initially, itching and a rash may occur at the site of infection. Hookworm infection is an infection by a type of intestinal parasite known as a hookworm. Not walking barefoot, stopping outdoor defecation Īlbendazole, mebendazole, iron supplements Walking barefoot in warm climates with poor sanitation

Itchiness, localized rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea Īncylostoma duodenale (old world hookworm), Necator americanus (new world hookworm)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
